What are stem cells?
10 October 2019 | Written by La redazione
Stem cells are the new frontier of medicine, in them there is the potential to face many diseases. Let's find out what they are.
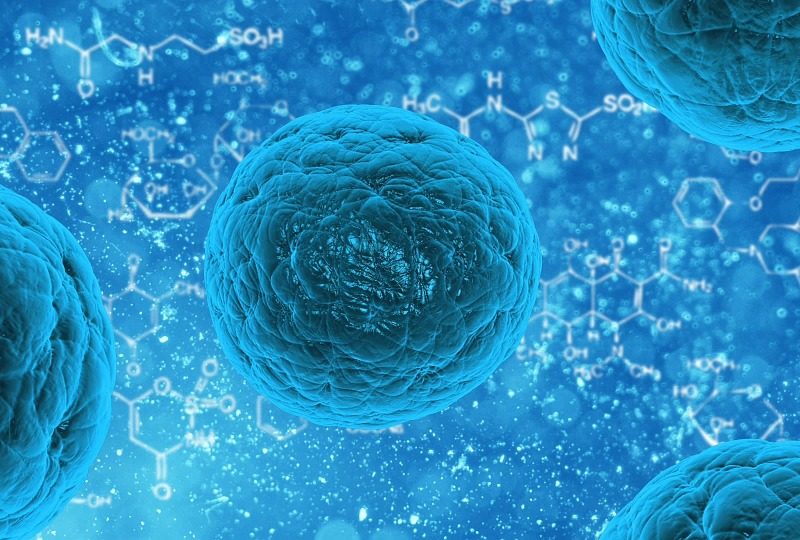
The research is focusing more and more on stem cells, the therapies created based on these cells, in fact, are proving to be promising in various fields. In order to better understand these therapies and their actual effectiveness it is important to understand what stem cells are and what makes them so special.
Stem cells, these unknown. We can imagine stem cells as primordial cells, undifferentiated cells, able, that is, to transform into cells of different tissues or organs. A stem cell can become skin, muscle, bone or any other cell in our body. Fro this ability derives their potential for the therapies being worked on. It is important, however, to clarify some details, because not all stem cells are the same.
Features. To be called a stem cell, a cell must have two characteristics: self-renewal and pluripotency. Self-renewal is the ability to renew itself to infinity while maintaining the characteristics of a stem cell. Pluripotency, on the other hand, is the most interesting part of these cells and that implies their curative potential: in fact, each stem cell is able to transform into any other cell of our body.
Not all stem cells, however, can turn into any cell: this depends on their “power”. There are in fact totipotent cells, which are able to become part of any organic tissue, but also pluripotent cells, which can be transformed into cells of many organs or tissues but not of all. Finally, there are unipotent stem cells that can become cells of one type.
Where can be found. In the adult human body, stem cells are found in the bone marrow, in the brain, in the deepest layer of the skin, in the dental pulp. Another source of stem cells is the umbilical cord and the amniotic fluid. To find totipotent stem cells, those with the greatest therapeutic potential given their ability to become any other type of cell and repair any type of damaged tissue, it is necessary to look at the beginning of the formation of a human being: they are, in fact, in the embryos humans, hence the name “embryonic stem cells”.
Since 2004, in Italy, the law on assisted fertilization has placed an absolute ban on the use of human embryos in scientific research on stem cells. This is a question that is clearly controversial from an ethical point of view and on which it is necessary to stimulate a constant dialogue. The hope is that one day we will be able to replace any sick tissue or organ in the body, recreating it in the laboratory.
Watch the video: